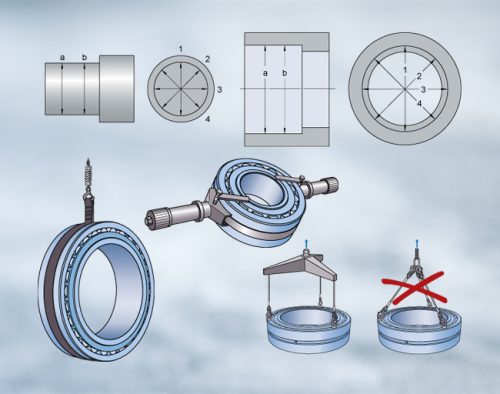
Rolling Bearing Storage
Store bearings in their original package in order to protect them against contamination and corrosion. Open package only at the assembly site immediately prior to mounting. Larger bearings with relatively thin-walled rings should not be stored upright but flat and supported over their whole…
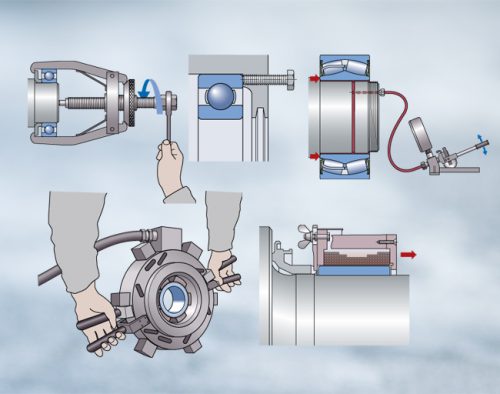
Rolling Bearing Mounting
The various bearing types and sizes require different mounting methods. Depending on the individual conditions these can be mechanical, hydraulic or thermal. As the hardened bearing rings are sensitive to blows, these must never be applied directly to the rings. On mounting of…
Rolling Bearing Dismounting
If the bearings are intended for re-use, dismounting must be performed most carefully; it is imperative that the extracting tool be applied to the ring to be extracted to prevent the rolling elements from brinelling the raceways. In addition, thin-walled outer rings involve the…
Lubrication
The primary purpose of the lubricant is to build a load-carrying film separating the bearing components in rolling and sliding contact in order to minimize friction and wear. The lubricant should also protect the bearing against corrosion. If required, it should also…
Rolling Bearing Damage
The life of a rolling bearing depends on the total number of stress cycles and the loads incurred by rolling elements and raceways. The standardized calculation method for dynamically stressed bearings is based on material fatigue (pitting) causing the damage. Normal fatigue manifests itself…